Food diversity is key to well rounded nutrition and health.
This article goes into cat specific nutrition. We recommend reading this article first to get a general understanding about feeding animals.
Here are some things to know as you cook for your cat.
CATS ARE CARNIVORES
Dogs have a preference for sweet foods. Cats do not. Cats prefer flavours that are typically perceived as bitter. This may reflect the cat’s evolutionary adherence to a more carnivorous feeding pattern.
NUTRITIONAL IDIOSYNCRASIES
Certain nutritional idiosyncrasies mean cats have more stringent dietary requirements.
- taurine need
- arachidonic acid need
- preformed vitamin A need
These needs can only be met by consuming animal tissue.
It is possible to develop a vegetarian diet for cats but this requires special supplementation of purified forms of taurine, arachidonic acid, and preformed vitamin A.
ROLE OF PROTEIN
- according to studies, the protein requirement of cats is substantially higher than that of other mammals, including the dog
- cat bodies maintain normal blood glucose through the consistent breakdown of proteins for energy
- taurine and arachidonic acid are essential (protein) for cats as their bodies cannot produce these in adequate amounts
- taurine and arachidonic acid are found only in animal tissue
- there is no evidence showing that high protein intake initiates or contributes to the progression of kidney dysfunction
- baking causes taurine levels in meats to degrade less than boiling
- pork lion raw = 600 mg / kg ~ baked = 200 mg / kg ~ boiled = 100 mg / kg
- clams raw = 2400 mg / kg ~ baked = 1000 mg / kg ~ boiled = 440 mg / kg
- lack of arginine in the diet causes an immediate and severe deficiency response in cats
- check that recipes provide the minimum recommended levels of arginine and taurine
ROLE OF FATS
- read this article to get a better understanding about feeding animals
ROLE OF CARBOHYDRATES
- dogs and cats do not require carbohydrate in their diets
- dry pet foods contain the highest amount of carbohydrate
Recipes for cats should typically have much lower levels of starch and fibre than for dogs. Diets with significant levels of starch can be a contributor in the development of diabetes in cats.
TYPICAL NUTRIENT CONTENTS OF COMMERCIAL CAT FOOD
- these are on a dry matter basis ~ which is the percentages of nutrients when its moisture content is 0%
| FAT | ||
| PROTEIN | ||
| CARBOHYDRATE |
CATS & VITAMIN A
- cats cannot convert carotenoid pigments to active vitamin A
- largest quantities of preformed vitamin A are found in fish liver oils and animal livers
- cats are unable to protect themselves from absorbing toxic levels of vitamin A when fed too much foods with concentrated levels of the vitamin
CATS & VITAMIN E
- feeding high levels of fish oil and fatty fish may cause a threefold to fourfold increase in a cat’s requirement for vitamin E
- vitamin E protects the body from oxidative damage that occurs with high levels of unsaturated fats typically found in fish oil and fatty fish
PETS & MINERALS
- calcium, iron, copper and zinc need attention as homemade diets made up of three or four ingredients often lack these in inadequate levels
- calcium and phosphorus levels in meals also need to be at a minimum ratio of 1:1
- egg shells are a great natural way of adding much needed calcium to diets
ROLE OF VITAMINS & MINERALS
- have a look at this link to see the role different nutrients play in our bodies
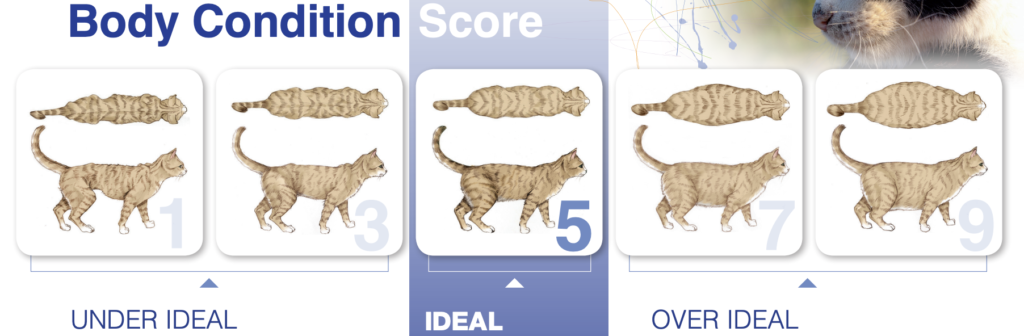
OBESITY
- obese dogs and cats frequently develop glucose intolerance and may predispose them to diabetes
- your cat is likely overweight if you are unable to see a concave abdominal tuck when viewed from side
If You Enjoyed Our Content
please consider buying us a coffee / sending us dog treats